DDD(Domain Driven Design)의 방법대로 서비스를 구현하기 위해서는 계층을 나눠 각각의 역할을 분리해야합니다. DDD를 이용한 개발에서 사용하는 세개의 계층에 대해 알아보겠습니다.
💻 Controller
Controller는 사용자의 요청 (post, get, delete, patch)을 받은 후, 요청에 대한 응답을 다시 사용자에게 반환하는 계층입니다.
Controller 계층은 도메인 로직을 직접 포함하지 않으며, Service 계층과 상호작용합니다.
아래는 Java와 Spring을 이용해 구현한 Controller 계층의 예시 코드 입니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/products")
public class ProductController {
private final ProductService productService;
@Autowired
public ProductController(ProductService productService) {
this.productService = productService;
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public ProductDto getProduct(@PathVariable Long id) {
Product product = productService.getProductById(id);
return new ProductDto(product);
}
@PutMapping("/{id}")
public ProductDto updateProduct(
@PathVariable("id") Long id,
@RequestBody ProductRequestDto productRequestDto
) {
Product product = productService.updateProduct(id, productRequestDto.getName(), productRequestDto.getPrice());
return new ProductDto(product);
}
}
위 코드에서 Controller 계층은 사용자의 get, put 요청을 받아 Service 계층과 상호작용을 한 후, 그 응답을 사용자에게 다시 보내는 것을 볼 수 있습니다. 또한 계층간 데이터를 전송할 때,DTO를 이용했음을 알 수 있습니다.
💻 Service
Controller와 Repository 계층 사이에서 도메인 객체를 처리합니다. Service 계층은 도메인 로직을 이용하는 계층으로 서비스에 필요한 비즈니스 로직이 이 계층에서 구현됩니다. 또한 Repository 계층을 주입받아 데이터에 접근할 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
@Service
public class ProductService {
private final ProductRepository productRepository;
@Autowired
public ProductService(ProductRepository productRepository) {
this.productRepository = productRepository;
}
public Product getProductById(Long id) {
Optional<Product> optionalProduct = productRepository.findById(id);
return optionalProduct.orElseThrow(() -> new ProductNotFoundException(id));
}
public Product updateProduct(Long id, String name, BigDecimal price) {
Product product = getProductById(id);
product.setName(name);
product.setPrice(price);
return product;
}
}
예시에서 볼 수 있듯이 Service 계층은 Repository 계층을 주입 받아 데이터에 접근하고 있습니다. 또한 updateProduct에서 도메인 모델 중 하나인 Product의 로직을 사용하고 있음을 볼 수 있습니다.
아래는 Product 도메인 모델로 Entity와 유사함을 알 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
@Entity
@Table(name = "products")
public class Product {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String name;
@Column(nullable = false)
private BigDecimal price;
public void setName(String name) {
if (name == null || name.trim().isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("상품 이름은 필수입니다.");
}
this.name = name;
}
public void setPrice(BigDecimal price) {
if (price == null || price.compareTo(BigDecimal.ZERO) <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("가격은 0보다 큰 값이어야 합니다.");
}
this.price = price;
}
public void changeName(String name) {
setName(name);
}
public void changePrice(BigDecimal price) {
setPrice(price);
}
}
🖊 비즈니즈 로직?
서비스를 구현하기 위한 핵심 로직들을 의미합니다.
온라인 서점에서 상품등록을 예시로 들어보면, 등록시에 중복 검사, 수량의 유효성 검증등이 비즈니스 로직에 해당합니다.
💻 Repository
도메인 객체를 저장하고 관리하는 계층으로, DB와 직접 상호작용해 데이터를 검색하고 저장하는 계층입니다.
1
2
3
4
@Repository
public interface ProductRepository extends JpaRepository<Product, Long> {
void findById(Long id);
}
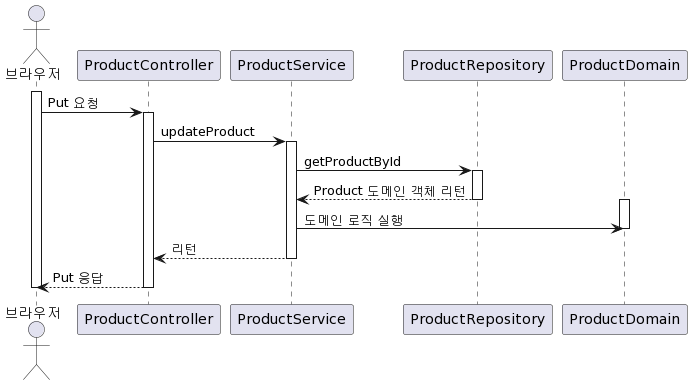
위 계층간 상호작용을 시퀀스 다이어그램으로 나타내면 다음과 같습니다.